The force on a 0.500-kg particle depends on position such that F(x) = (1.00 N/m2)x2 + ( 4.00 N/m)x for a particle constrained to move along the x-axis
If the particle starts from rest at x = 0.00, what will be its speed when it reaches the position x = 4.00 m?
A)
1.65 m/s
B)
22.6 m/s
C)
14.6 m/s
D)
11.3 m/s
E)
The particle will not reach the position x = 4.00 m.
C
You might also like to view...
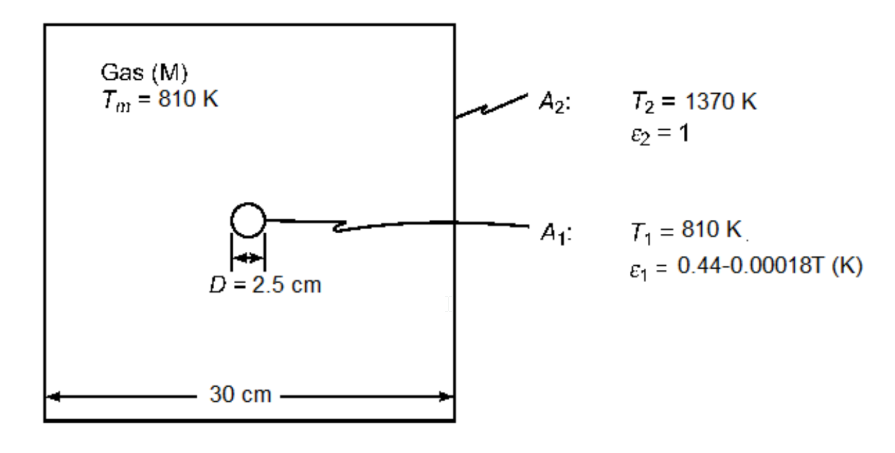
A small sphere (2.5 cm-diam) is placed in a heating oven. The oven cavity is a 30 cm cube filled with air at 101 kPa(abs); it contains 3 % water vapor at 810 K, and its walls are at 1370 K. The emissivity of the sphere is equal to 0.44 – 0.00018 T, where T is the surface temperature in K. When the surface temperature of the sphere is 810 K determine (a) the total irradiation received by the walls of the oven from the sphere, (b) the net heat transfer by radiation between the sphere and the walls of the oven, and (c) the radiant heat transfer coefficient.
GIVEN
A small sphere in a 30 cm cubic heat oven filled with air
Sphere diameter (D) = 30 cm – 2.5 cm= 27.5 cm
Air pressure = 101 kPa(abs) = 1.01*105 Pa
Air contains 3% water vapor
Air temperature (Tm) = 810 K
Oven wall temperature (T2) = 1370 K
Sphere emissivity (?1) = 0.44 – 0.00018 T (T in K)
Sphere surface temperature (T1) = 810 K
FIND
(a) Total irradiation received by the walls from the sphere (q2)
(b) The net heat transfer by radiation between the sphere and the walls (q12)
(c) The radiant heat transfer coefficient (hr)
ASSUMPTIONS
The gas is a gray body
The oven walls are black (?2 = 1)
The sphere is near the center of the oven
SKETCH
PROPERTIES AND CONSTANTS
the Stephan-Boltzmann constant
A child on a playground swings through a total of 32 degrees. If the displacement is equal on each side of the equilibrium position, what is the amplitude of this vibration?
a. 32 b. 16 c. 64
Which of the following expands more when the temperature is increased? Equal volumes of
A) iron. B) wood. C) ice water. D) helium. E) all expand the same.
A 5.0-kg stone is thrown upward at 7.5 m/s at an angle of 51° above the horizontal from the upper edge of a cliff, and it hits the ground 1.5 s later. Neglect air. Find the magnitude of its velocity vector just as it reaches the ground
What will be an ideal response?