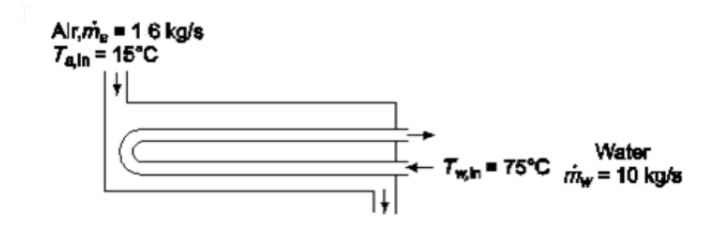
Water flowing at a rate of 10 kg/s through 50 tubes double-pass shell and tube heat exchanger heats air that flows through the shell side. The length of the brass tubes is 6.7 m and they have an outside diameter of 2.6 cm and an inside diameter of 2.3 cm. The heat transfer coefficient of the water and air are 470 W/(m2 K) and 210 W/(m2 K), respectively. The air enters the shell at a temperature of 15°C and a flow rate of 16 kg/s. The temperature of the water as it enters the tubes is 75°C. Calculate (a) the heat exchanger effectiveness, (b) the heat transfer rate to the air, and (c) the outlet temperature of the air and water.
GIVEN
• Shell-and-tube heat exchanger - one shell, two tube passes
• Water in brass tubes, air in shell
• Water flow rate ( m w)= 10 kg/s
• Number of double passes (N) = 50
• Tube length (L) = 6.7 m
• Tube diameters
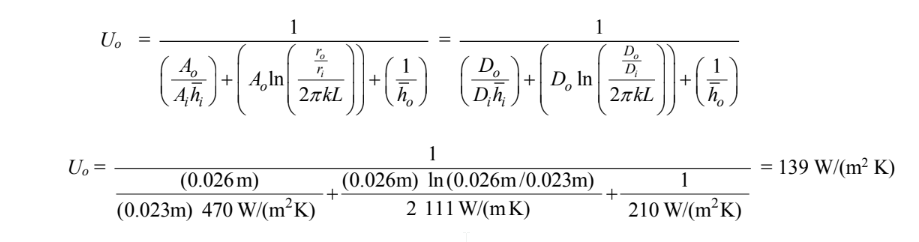
? Do = 2.6 cm = 0.026 m
? Di = 2.3 cm = 0.023 m
• Heat transfer coefficient
? Water ( )ih = 470 W/(m2 K)
? Air ( )oh = 210 W/(m2 K)
• Air inlet temperature (Ta,in) = 15°C
• Air flow rate ( m a)= 16 kg/s
• Water inlet temperature (Tw,in) = 75°C
FIND
(a) Effectiveness (e)
(b) The heat transfer rate (q)
(c) Outlet temperatures (Ta,out, Tw,out)
ASSUMPTIONS
• Tube length includes both passes
SKETCH
OPERTIES AND CONSTANTS
the specific heat of water at 75°C (cpw) = 4190 J/(kg K)
the specific heat of air at 15°C (cpa) = 1012 J/(kg K)
the thermal conductivity of brass (kb) = 111 W/(m K)
The heat capacity rates are
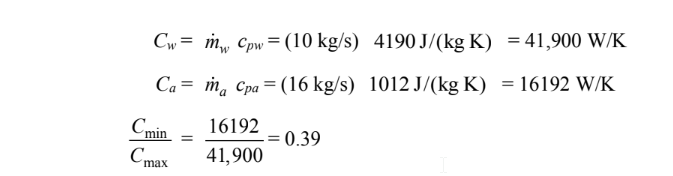
(a) The overall heat transfer coefficient is
The transfer area is A = N(? Do L) = 50[? (0.026 m)(6.7 m)] = 27.36 m2 The Number of transfer units is
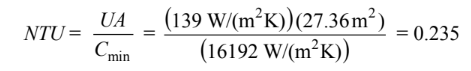
for Cmin/Cmax = 0.4 and NTU = 0.235, e ? 0.20 = 20% (b) The rate of heat transfer is
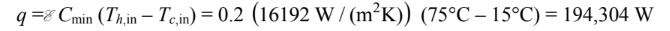
(c) For the water
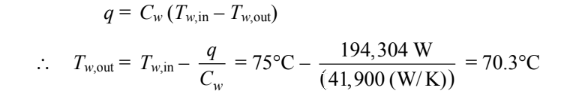
For the air
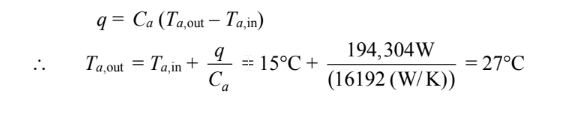
You might also like to view...
Which best describes the transit method?
a. observing changes in the brightness of the star when the orbiting planet crosses in front of the star b. observing the magnification of a distant star's brightness by gravitational lensing when an extrasolar planet passes precisely between Earth and a background star c. observing the back-and-forth motion that can be measured from Doppler shifts in a star's spectrum d. observing the intensity of brightness from a newborn distant star e. observing the magnification of a distant planet when it passes closely to our Solar System
How many grams of sodium chloride are needed to make 15 L of a solution that has a concentration of 3.0 g per liter of solution?
A) 30 g B) 141 g C) 5 g D) 45 g
The ionic layers of the atmosphere reflect
a) radio waves. b) charged particles. c) sound. d) light.
Electric field is dimensionally equivalent to which of the following?
a. N/C2 c. N×m2/C2 b. N×m/C d. N/C