Temperature Scales: At what, if any, temperature are the numerical readings on the Fahrenheit and Celsius scales the same?
A. -30°
B. -40°
C. -50°
D. -60°
E. They can never read the same because they are based on different zeroes.
Answer: B
You might also like to view...
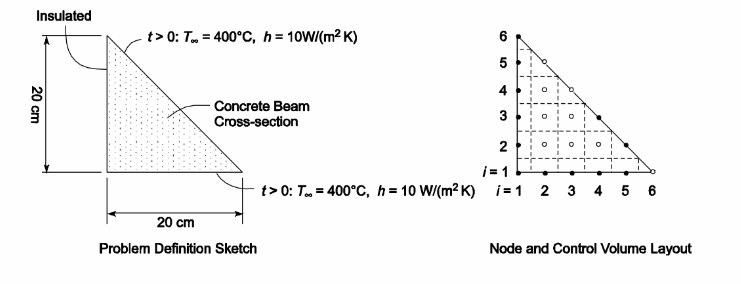
A long concrete beam is to undergo a thermal test to determine its loss of strength in the event of a building fire. The beam cross section is triangular as shown in the sketch. Initially, the beam is at a uniform temperature of 20°C. At the start of the test, one of the short faces and the long face are exposed to hot gases at 400°C through a heat transfer coefficient of 10 W/(m2 K) and the remaining short face is adiabatic. Produce a graph showing the highest and lowest temperatures in the beam as a function of time for the first 1 hour of exposure. For the concrete properties, use k = 0.5 W/(mK) and n = 5 x 10–7 m2/s. Use a node spacing of 4 cm. and use an explicit difference scheme.
GIVEN
Concrete beam suddenly exposed to hot gases
FIND
(a) Highest and lowest temperatures in the beam as a function of time
SKETCH
An atom of "anti-hydrogen" would be made of
A) an anti-proton and a positron. B) a positron and an electron. C) a proton and a positron. D) a high-frequency photon and a low-frequency photon. E) an anti-proton and a muon.
How much electromagnetic energy is contained in each cubic meter near the Earth's surface if the intensity of sunlight under clear skies is 1 000 W/m2?
a. 3.3 × 10^-6 J b. 3.3 J c. 0.003 J d. 10-4 J e. 3.0 × 10^5 J
What is the cause for the slow movement of reference marks, such as the celestial poles and equator, to move across the sky?
a. precession b. evolution c. climate change d. continental drift e. angular revolution