In tomatoes, red (R) is dominant to yellow (r), tall (D) is dominant to dwarf (d), and smooth (H) is
dominant to peach or hairy (h).
(a) How many different genotypes are there in relationship to these three characteristics?
(b) How many different phenotypes are there in relationship to these three characteristics?
(c) How many different homozygous pure-breeding forms can be produced? What will be an ideal response?
(a) 27
(b) 8
(c) 8
You might also like to view...
A mutated form of the CFTR gene is associated with
a. recognition proteins. b. gap junction formation. c. peripheral proteins in plasma membranes. d. sinus problems. e. passive transporters.
Imagine a researcher is trying to genetically engineer this virus so it attacks the lung cells of a human in order to "infect" the host with a particular gene to cure a genetic disorder. Explain which structure the researcher would be most interested in working with in order to get the virus to attack the lung cell of a human.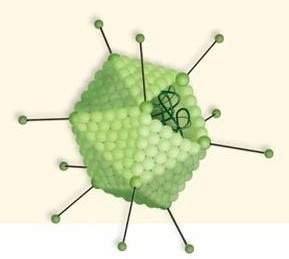
What will be an ideal response?
What localization occurs for proteins that are normally nuclear when their nuclear localization signal is deleted and the protein is injected into the cytoplasm of cultured cells?
a. Nucleus b. Cytoplasm c. In a ring around the outside of the nuclear envelope d. Extracellular
This form of carbon results from cell respiration.
A) Producers B) Carbon dioxide C) Transpiration D) limestone