When a good ends up overconsumed and depleted, we can assume it is a:
A. scarce good.
B. common resource.
C. public good.
D. private good.
Answer: B
You might also like to view...
A firm's horizontal dimension refers to
A) its size in its primary market. B) its size in all markets in which is competes. C) the level of supply chain integration the firm undertakes. D) the number of stages in the production process that are upstream from the stages the firm undertakes.
Your U.S.-based company is selling parts to a company in Chile and the company will pay you US$10,000 in 3 months. The current exchange rate is 490 pesos/US$. If the exchange rate at the time of payment is 510 pesos/US$
A) you earn additional profit. B) the Chilean company will end up paying more for the goods. C) the Chilean company will end up paying less for the goods. D) you earn less profit.
In a free market, if the price of a good is above the equilibrium price, then;
A. sellers, dissatisfied with growing inventories, will lower their prices. B. the government will set a lower price to reestablish the market equilibrium. C. sellers, dissatisfied with growing inventories, will raise their prices. D. buyers, hoping to ensure they acquire the good, will bid the price lower.
Refer to the below table. What would the wage rate be if all the workers could work in all three labor markets, and they get spread out evenly?
Suppose there are only three labor markets (A, B, and C) in the economy and each of these markets is purely competitive. The table below contains the demand (or marginal-revenue-product) schedule for labor in each of these three markets. Assume there are 24 million homogeneous workers in the economy and that one-half of these workers are male and one-half are female
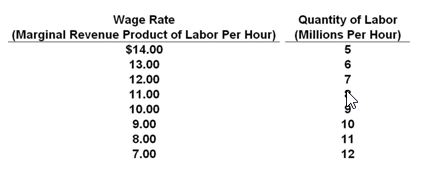
A. $7.00 for females and $13.00 for males
B. $8.00 for females and $11.00 for males
C. $11.00 for females and $11.00 for males
D. $13.00 for females and $13.00 for males