Which is not a criticism of the marginal productivity theory of distribution?
A. It assumes that the existing distribution of ownership factors is fair and just when it may not be.
B. It does not tell us much about real policy matters.
C. A factor’s MRP does not in any way correspond to productive effort.
D. It is inconsistent with most empirical observations.
Answer: D
You might also like to view...
If you have $10,000 to start a lawn-cutting business, the interest rate is 4 percent, your cost of equipment is $3,000, and the earnings you sacrifice from working at another job are $32,000, your yearly cost of doing business would be
A) $13,000. B) $13,400. C) $35,400. D) $45,000.
Total government spending (federal, state, and local) sums to approximately
a. 10 percent of the U.S. economy. b. 20 percent of the U.S. economy. c. 40 percent of the U.S. economy. d. 50 percent of the U.S. economy.
Refer to the figure below. In response to gradually falling inflation, this economy will eventually move from its short-run equilibrium to its long-run equilibrium. Graphically, this would be seen as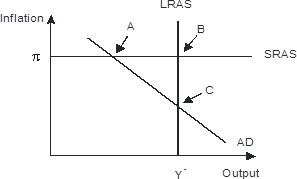
A. long-run aggregate supply shifting leftward B. Short-run aggregate supply shifting downward C. Aggregate demand shifting rightward D. Aggregate demand shifting leftward
From 1979-2007, labor income for U.S. households became more evenly distributed.
Answer the following statement true (T) or false (F)