A random variable that can only take on a countable number of values is known as what type of random variable?
A. Continuous
B. Population parameter
C. Probability density function
D. Discrete
Answer: D
You might also like to view...
Trout and amoebas are both heterotrophs, and can inhabit similar environments (for example, a freshwater pond). However, these organisms are very different when it comes to their shape and size. Why?
A. Trout and amoebas utilize different sources of CO2. B. Trout and amoebas utilize different sources of C6H12O6 (or other organic compounds). C. Trout and amoebas utilize different sources of O2. D. Trout and amoebas have different metabolic pathways. E. Trout and amoebas are exposed to different environmental conditions, even when they inhabit the same pond.
Which master gene sculpts the details of the body's form? a. All of the genes in the body control the details of the body's form
b. There is no master genes for body form. c. Dlx d. Hox e. Hoxc6
In multiple sclerosis the myelin sheaths around the axons of the brain and spinal cord are damaged and demyelination results
How does this disease manifest at the level of the action potential? I) Action potentials move in the opposite direction on the axon. II) Action potentials move more slowly along the axon. III) No action potentials are transmitted. A) only I B) only II C) only III D) only II and III
The accompanying figure shows data from an experiment in which researchers measured how far dynein (a motor protein) traveled in the presence and absence of dynactin (another type of protein). The y-axis shows the percent of the time that the researchers
observed either dynein or dynein + dynactin "walking" a certain distance on a microtubule. What can you conclude from these data?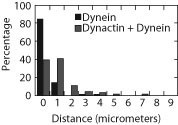
A) The addition of dynactin caused dynein to travel farther along the microtubule.
B) Dynein traveled farther in the absence of dynactin.
C) A higher fraction of the dynein proteins were motile in the absence of dynactin.
D) Dynactin would have the same effects on dynein movement on microfilaments.