Refer to the figure. Suppose that the economy is currently operating at the intersection of AS and AD 2 , and that the full-employment level of output is Y. If the government wants to move the level of real GDP back to Y and reduce demand-pull inflation, in the presence of a ratchet effect, it should:
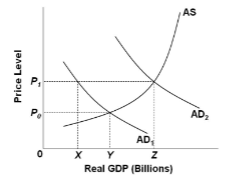
A. reduce taxes or increase government spending.
B. enact a contractionary fiscal policy that will shift aggregate demand left to AD 1 .
C. enact a contractionary fiscal policy that will shift aggregate demand to the left, but not as far as AD 1 .
D. enact a contractionary fiscal policy that will shift aggregate demand to the left, farther left
than AD 1 .
C. enact a contractionary fiscal policy that will shift aggregate demand to the left, but not as far as AD 1 .
You might also like to view...
A negative externality clearly occurs when
A) a person's action unintentionally benefits other people. B) a person behaves in the public interest. C) a person's action unintentionally imposes costs on other people. D) a person couldn't care less about anybody else.
For economists, discrimination is difficult to rationalize because:
a. it is costly to those who discriminate. b. the firms can actually reap greater profits by discriminating between their workers. c. in a freely functioning labor market, there is no such thing as discrimination. d. economists know that in the real world, personal prejudices do not exist. e. wages will not be allowed to fall below their natural equilibrium rate.
An example of a discretionary fiscal policy is when...
What will be an ideal response?
Refer to the below graph. At the profit-maximizing level of short-run output, this monopolistic ally competitive firm will be making a profit of:
The graph depicts a monopolistic ally competitive firm.
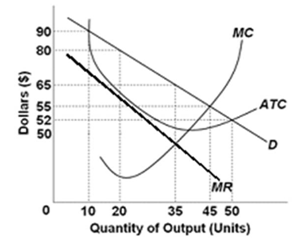
A. $275
B. $350
C. $500
D. $525