When we see X-rays from an accretion disk in a binary system, we can't immediately tell whether the accretion disk surrounds a neutron star or a black hole. Suppose we then observe each of the following phenomena in this system
Which one would force us to immediately rule out the possibility of a black hole? A) bright X-ray emission that varies on a time scale of a few hours
B) spectral lines from the companion star that alternately shift to shorter and longer wavelengths
C) sudden, intense X-ray bursts
D) visible and ultraviolet light from the companion star
C
You might also like to view...
Galileo's telescopic discoveries of mountains on the Moon and spots on the Sun were controversial because they suggested that the Sun and Moon
a. were the same kind of object. b. were not perfect spheres. c. were inhabited. d. orbited each other. e. did not orbit Earth.
Weight and g: Two planets have the same surface gravity, but planet B has twice the radius of planet A. If planet A has mass m, what is the mass of planet B?
A. m/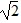
B. m
C. m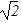
D. 4m
E. m/4
Air with a density of 1.20 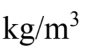 flows through a 10.0 cm diameter pipe with a velocity of 1.20 m/s. What is the mass flow rate?
flows through a 10.0 cm diameter pipe with a velocity of 1.20 m/s. What is the mass flow rate?
A. 0.0148 kg/s B. 0.0131 kg/s C. 0.0120 kg/s D. 0.0113 kg/s E. 0.0098 kg/s
The principle or law that says "an induced emf in a circuit loop produces a current whose magnetic field opposes further change of magnetic flux" is credited to:
a. Faraday. b. Lenz. c. Ampere. d. Volta.