Cross price elasticity measures
A. How complements and substitutes differ from one another.
B. How sensitive quantity demanded is to a change in price.
C. The change in quantity demanded for one good relative to a change in the price of another good.
D. The change in quantity demanded when income changes.
Answer: C
You might also like to view...
Refer to Table 11-8. Elegant Settings experiences
A) increasing returns beyond an output level of 400. B) economies of scale up to an output level of 400. C) diminishing returns up to an output level of 400. D) economies of scale at an output of 300 or less and diseconomies of scale at an output level above 400.
Which statement is true?
A. Right-to-work laws promote the formation of union shops. B. A monopsony is the only buyer of a product for which there are no close substitutes. C. Under a union shop, an employer may hire only union workers. D. Monopsonies are illegal under the Taft-Hartley Act.
At the equilibrium level of real GDP, which of the following is true?
A. Unplanned inventory investment is positive. B. Unplanned inventory investment is negative. C. Aggregate output equals aggregate expenditures. D. Aggregate output plus consumption spending equals aggregate expenditures.
Refer to the information provided in Figure 2.4 below to answer the question(s) that follow.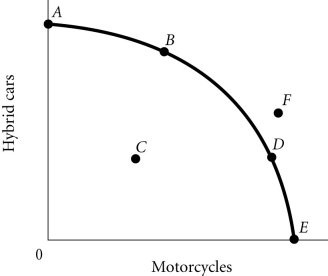 Figure 2.4According to Figure 2.4, Point E necessarily represents
Figure 2.4According to Figure 2.4, Point E necessarily represents
A. only motorcycles being produced. B. overallocation of resources. C. an impossible production point. D. technological advancement.