Monopoly pricing prevents some mutually beneficial trades from taking place. These unrealized, mutually beneficial trades are
a. less of a concern for a monopoly than competitive market.
b. offset by the higher profits earned by a monopolist.
c. a function of the reduction in the quantity produced by a monopolist in comparison to a competitive market.
d. All of the above are correct.
c
You might also like to view...
Is a firm economically inefficient if it can cut its costs by producing less? Why or why not?
What will be an ideal response?
Refer to the table below. What is the profit-maximizing number of quality units for Fresh Laundry to produce?
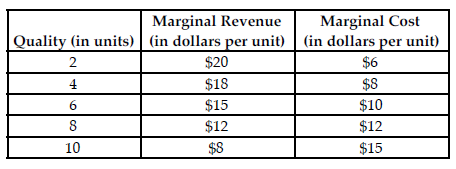
Fresh Laundry is a firm that produces laundry detergent. The table above summarizes Fresh Laundry's product quality marginal revenue and marginal cost at various quality levels.
A) 4
B) 6
C) 10
D) 8
When does market equilibrium change in a given market?
What will be an ideal response?
Let: (1 ) Pt be the price of one unit of a market basket of goods (i.e., a composite commodity) in year t; (2 ) Pet+1 be the expected price of one unit of a market basket of goods in year t + 1; (3 ) ?et+1 be the expected rate of inflation between period t and t + 1; and (4 ) it be the one-year nominal interest rate. Suppose an individual borrows the equivalent of one unit of a composite
commodity today. Given this information, which of the following expressions represents (i.e., is equal to) the amount of the composite commodity one must repay in one year? A) (1 + it)(Pet+1)/(Pt) B) (1 + ?et+1)/(1 + it) C) {(1 + ?et+1)/(1 + it)} - 1 D) {(1 + it)(Pt)/(Pet+1)} - 1 E) none of the above