Figure 10-3
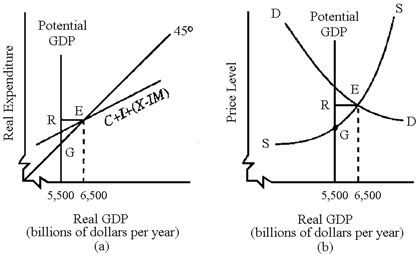
In Figure 10-3, we would expect the aggregate supply curve in graph (b) to eventually
a.
shift to the right, eliminating the recessionary gap.
b.
shift to the left, eliminating the inflationary gap.
c.
become steeper in the upper portion, eliminating the inflationary gap.
d.
become flatter in the upper portion, eliminating the recessionary gap.
b
You might also like to view...
In the balance sheet for the FBN bank above, the entries are in millions of dollars. If the desired reserve ratio equals 10 percent, FBN Bank has excess reserves of
A) $280 million. B) $200 million. C) $360 million. D) $0.
Pricing and output determination under an oligopoly is more complicated than pricing and output determinations in other industries. The primary reason for the complication is the:
A. fewness of firms. B. brand loyalty of consumers. C. powerful effect of advertising. D. mutual interdependence of firms.
A decrease in the level of real GDP in the economy leads to:
A. a leftward shift in the demand for money curve. B. a rightward shift in the demand for money curve. C. a leftward movement along the demand for money curve. D. a rightward movement along the demand for money curve.
In the short run, if the price level increases, then nominal wages:
A. Stay fixed, therefore firms' revenues and profits will increase B. Stay fixed, and the firms' revenues and profits also stay the same C. Increase, causing firms' revenues and profits to fall D. Decrease, causing firms' revenues and profits to rise