The marginal benefit of acquiring additional information tends to
a. be zero if the marginal cost of information is zero
b. increase and then decrease as additional information is obtained
c. be smaller, the smaller the quantity of information the individual already has obtained
d. increase as additional information is obtained
e. decrease as additional information is obtained
E
You might also like to view...
Which of the following is the best example of scarcity?
A) The Talking Teddy is a surprise holiday hit, resulting in long lines of consumers trying to purchase the limited number of available Teddies. B) Fred only gets a 10-hour lunch break and each day must decide between working out at the gym or socializing with his colleagues. C) The local market's buy-one-get-one-free sale on strawberries results in more people wanting the berries than producers are able and willing to supply. D) There is a bumper crop of strawberries, and stores have more berries than they can sell.
When people forget that money is ________ they often make ________ decisions.
A. liquid; rational B. liquid; irrational C. fungible; irrational D. fungible; liquid
Figure 10-15
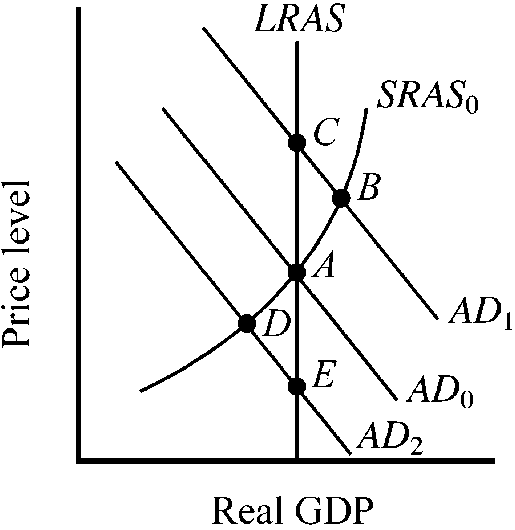
The economy's short-run (SRAS ) and long-run (LRAS) aggregate supply curves are shown in , along with three alternative aggregate demand curves and the accompanying equilibrium points. At which point will resource prices naturally tend to decrease?
a.
A
b.
B
c.
C
d.
D
Why is a discounted airline fare a price discrimination that can be offered?
(A) Because people who fly on business want the price discounts but do not qualify. (B) Because senior citizens qualify for discounts on certain types of flights but not on others. (C) Because people do not necessarily want to go where the discounts will allow them to go. (D) Because vacationers are willing to put up with the restrictions that the airlines impose.