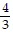Find the sample space for the experiment.There are 3 balls in a hat; one with the number 1 on it, one with the number 2 on it, and one with the number 5 on it. You pick a ball from the hat at random and then you roll a die.
A. {1 2 5 1, 1 2 5 2, 1 2 5 3, 1 2 5 4, 1 2 5 5, 1 2 5 6}
B. {1 1, 1 2, 1 3, 1 4, 1 5, 1 6, 2 1, 2 2, 2 3, 2 4, 2 5, 2 6, 5 1, 5 2, 5 3, 5 4, 5 5, 5 6, 3 1, 4 1, 6 1, 3 2, 4 2, 6 2, 3 5, 4 5, 6 5}
C. {1 1, 1 2, 1 5, 2 1, 2 2, 2 5, 5 1, 5 2, 5 5}
D. {1 1, 1 2, 1 3, 1 4, 1 5, 1 6, 2 1, 2 2, 2 3, 2 4, 2 5, 2 6, 5 1, 5 2, 5 3, 5 4, 5 5, 5 6}
Answer: D
You might also like to view...
Solve the formula for the specified letter.L = 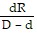 for d
for d
A. d = LD - R - L
B. d = 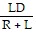
C. d = 
D. d = 
Provide an appropriate response.Given that we know the Fundamental Theorem of Calculus, why would we want to develop numerical methods for definite integrals?i) Antiderivatives are not always expressible in closed form.ii)Numerical methods are a good excuse to use our graphics calculator.iii) The function f(x) may not be continuous on [a,b].
A. Only ii is correct. B. Only i is correct. C. Only iii is correct. D. Both i and iii are correct.
Write an equation, in slope-intercept form if possible, of the line through the pair of points.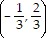 and
and 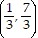
A. y = 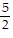 x +
x + 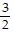
B. y = 5x + 9
C. y = 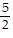 x
x
D. y = 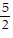 x -
x - 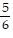
Determine if the sequence is arithmetic, geometric, or neither. If arithmetic or geometric, determine the first term and the common difference or common ratio.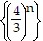
A. neither arithmetic nor geometric
B. Geometric; a = 1, r = 
C. Geometric; a = 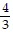 , r =
, r = 
D. Arithmetic; a = 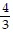 , d =
, d =