Ali inherits $10,000 from his great-great aunt in 2008. His great-great aunt's will requires that Ali spend the money before December 31, 2009. He has two spending options: He can either spend the amount in 2008 or in 2009. Suppose this is Ali's only source of income and the interest rate on loans or savings is 10 percent.(a) How much could Ali spend in 2008 if he only consumes in 2008? How much could Ali spend in 2009 if he only consumes in 2009?(b) What is the opportunity cost of consuming $1.00 in 2008 in terms of forgone consumption in 2009? Draw Ali's budget constraint and optimal consumption bundle, considering that the spending in 2008 is measured along the horizontal axis.(c) Ali decides to spend $6,000 in 2008 and $4,400 in 2009. Show this optimal consumption bundle using a
budget constraint and indifference curve diagram.
What will be an ideal response?
(a) If Ali only consumes in 2008, he can spend $10,000 in 2008, whereas if he consumes only in 2009, he can spend (1 + 0.10) × 10,000 = (1.10) × 10,000 or $11,000 in 2009.
(b) You give up $1.10 in 2009 consumption for every dollar you spend in 2008.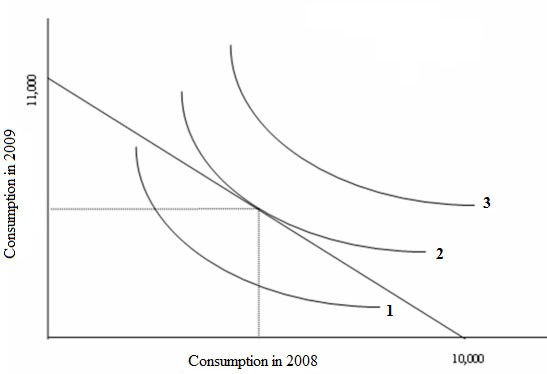
(c)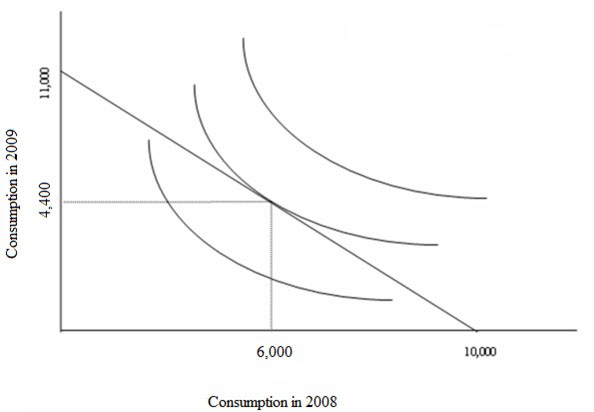
You might also like to view...
The traditional Keynesian approach concludes that an increase in government spending
A) generates a greater increase in investment spending. B) generates a greater increase in total spending because consumption spending increases as incomes increase. C) has no effect on total spending because consumers increase saving by an equal amount. D) generates an equal increase in total spending because government spending makes up part of total spending.
Other things constant, when households decide to save more, the supply of credit rises, interest rates ________ and business investment ________
A) rise; rises B) rise; falls C) fall; rises D) fall; falls
If MPS is equal to 0.15 and MPI is equal to 0.10, an initial change of $19,000 in government expenditure would result in a total change of _____ in income
a. $19,000 b. $16,150 c. $20,000 d. $76,000 e. $126,667
In a cartel, firms jointly act as
A) a monopolistic competitive firm. B) a perfectly competitive firm. C) a monopoly firm. D) an oligopolistic firm.