A piece of wire 15 m long is cooled from 40°C to –9°C and the change in length is –12.7 mm.
(a) What is the linear coefficient of thermal expansion for this material?
(b) Identify the material based upon the measured coefficient of thermal
expansion.
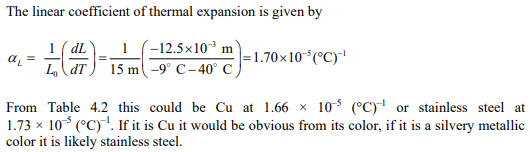
You might also like to view...
Opacity is
a. the balance between the pressure and force of gravity inside a star. b. the force that binds protons and neutrons together to form a nucleus. c. the force that binds an electron to the nucleus in an atom. d. a measure of the resistance to the flow of radiation (photons) through a gas. e. the temperature and density at which a gas will undergo thermonuclear fusion.
An object is dropped from a helicopter. When it reaches terminal velocity
A) the acceleration finally reaches g. B) gravity no longer acts upon it. C) all of the upward forces add up to zero. D) the total force is zero. E) the acceleration of gravity, g, becomes 0.
On a Hertzsprung-Russell diagram, where would you find red giant stars?
A) upper right B) lower right C) upper left D) lower left
The twinkling of starlight and the focusing of images by lenses are both due to ________ of light
A) transmission B) refraction C) aberration D) reflection E) polarization