Along a perfectly competitive industry's long-run supply curve
A) economic profits are positive.
B) economic profits are zero.
C) entrepreneurs earn an above-average rate of return.
D) the number of firms is constant.
B
You might also like to view...
In what way does long-run equilibrium under monopolistic competition differ from long-run equilibrium under perfect competition?
A) Firms in perfect competition achieve allocative efficiency while firms in monopolistic competition achieve brand efficiency. B) Firms in perfect competition achieve productive and allocative efficiency while firms in monopolistic competition achieve neither allocative nor productive efficiency. C) The only difference is that in a monopolistically competitive market there are many brands to choose from while in a perfectly competitive market there is one standard product. D) Firms in perfect competition achieve productive efficiency while firms in monopolistic competition achieve allocative efficiency.
If a profit-maximizing firm finds that price exceeds average variable cost and marginal cost is greater than marginal revenue, it should: a. reduce output, but continue producing in the short run. b. increase output
c. shut down. d. not alter its production level since it is earning a profit.
Answer the following statements true (T) or false (F)
1) Economic models of illegal immigration suggest that domestic-born workers avoid certain types of work more because the inflow of immigrants has reduced wages, rather than because the work is unpleasant. 2) Removing all illegal immigrants would expand domestic-born employment by an amount equal to the number of illegal immigrants removed. 3) Illegal immigration helps improve the standard of living for U.S. citizens by keeping prices lower. 4) Illegal immigrants overall contribute more in taxes than they receive in services from state and local governments.
Refer to the information provided in Figure 31.2 below to answer the question(s) that follow.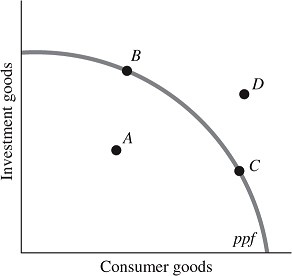 Figure 31.2Refer to Figure 31.2. Suboptimal production occurs when the economy is at Point
Figure 31.2Refer to Figure 31.2. Suboptimal production occurs when the economy is at Point
A. A. B. B. C. C. D. D.