During the last 30 years computers have changed most production processes. Use an isocost-isoquant diagram to show the effect the spread of computers have had on labor during the last 30 years.
What will be an ideal response?
Many answers are possible. But here is one possible one:
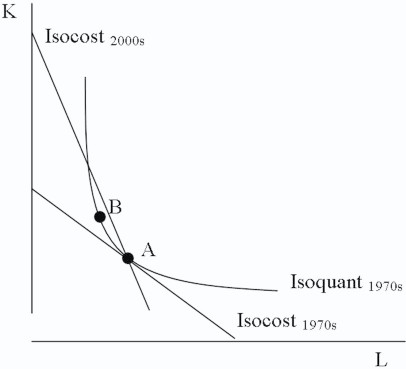
| ? |
You might also like to view...
The "tragedy of the commons" refers to a phenomenon where
A) people do not internalize an externality. B) people have distinct property rights to a resource. C) people overuse a common resource. D) individuals are not allowed to use a common resource.
The hidden-cost fallacy occurs when
a. A firm considers irrelevant costs b. A firm ignores relevant costs c. A firm considers overhead or depreciation costs to make short-run decisions d. Both a and c
The ____ is equal to the sum of the squares of the market shares of all the firms in an industry
a. market concentration ratio b. Herfindahl-Hirschman index c. correlation coefficient d. standard deviation of concentration e. none of the above
When a government subsidy is granted to the sellers of a product, buyers can end up capturing some of the benefit because
a. the market price of the product will fall in response to the subsidy. b. the market price of the product will rise in response to the subsidy. c. the market price of the product will not change in response to the subsidy. d. producers will reduce the supply of the product.