Suppose a satellite orbits the earth so closely that it experiences some drag due to the earth’s upper atmosphere. This will drain away some of the orbital energy of this system, converting it to thermal energy. If this happens fairly slowly, the satellite’s orbit will remain nearly circular. What happens to the radius of this satellite’s orbit as time passes in this case?
A. It slowly decreases.
B. It remains the same: just the satellite’s speed decreases.
C. It slowly increases
A. It slowly decreases.
You might also like to view...
An ideal diatomic gas has a molar specific heat at constant pressure Cp of:
A. R B. 3R/2 C. 5R/2 D. 7R/2 E. 9R/2
Which of the following statements does not apply to the formation of gas giants like Jupiter, compared to terrestrial planets?
A) accreted from icy planetesimals B) formed in a region with lower orbital speeds C) surface dramatically altered during bombardment D) caused icy planetesimals to slingshot away from the Sun, to become Oort cloud comets E) formed in regions cold enough for water to freeze
If the tension, in figure below
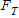 , is 15 N and the magnitude of the acceleration, a, is 3.0 m/s2, what is the mass, m, of the suspended object? Assume that all surfaces and the pulley are frictionless.
, is 15 N and the magnitude of the acceleration, a, is 3.0 m/s2, what is the mass, m, of the suspended object? Assume that all surfaces and the pulley are frictionless.
?
a.
3.1 kg
b.
2.5 kg
c.
2.8 kg
d.
2.2 kg
e.
3.7 kg
What characteristic of Uranus makes it stand out from all the other Jovian planets?
a. the farthest planet from the Sun b. rotates on its side c. has the longest orbital period d. Its moon is the same size as the planet e. atmosphere contains methane