Hudson has two job offers when he graduates from college. Hudson views the offers as identical, except for the salary terms. The first offer is at a fixed annual salary of $45,000. The second offer is at a fixed salary of $25,000 plus a possible bonus of $40,000. Hudson believes that he has a 50-50 chance of earning the bonus. If Hudson takes the offer that maximizes his expected utility and he is risk-loving, then
A. he will take the first offer.
B. he will take the second offer.
C. he is indifferent between the offers-both yield the same expected utility.
D. Indeterminate from the given information-we cannot say what he will do.
Answer: B
You might also like to view...
The figure above shows Sam's budget line. Which of the following would result in Sam's budget line rotating inward and not changing its vertical intercept?
A) a decline in his preference for coffee B) a fall in the price of a gallon of gasoline C) a decrease in Sam's income D) an increase in the price of a pound of coffee
An economy's resources:
a. are limited in quantity. b. are always efficiently utilized. c. consist of land, labor, capital, and money. d. are unrelated to its standard of living. e. are unlimited when we use the latest technology.
Harry gets $1,000 in currency from his grandfather when he graduates from college. He deposits these funds into his checking account. Considering Harry's personal balance sheet, his assets:
A. And liabilities increased by $1,000 when he deposited the funds into his checking account. B. increased by $1,000 when he deposited the $1,000 into his checking account. C. Increased when he received the $1,000 in currency from his grandfather. D. Increased by $1,000 and his liabilities decreased by $1,000 when he deposited the funds into his checking account.
Which of the following could produce the result indicated by the arrow in the Actual & Potential GDP graph? Check all that apply.
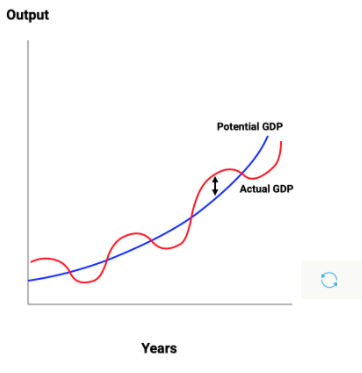
a. An increase in Consumer Spending
b. A decrease in Government Spending
c. An Increase in Taxes
d. A decrease in the money supply
e. An increase in Investment Spending
f. A decrease in Consumer Spending