When an expansionary fiscal policy increases market interest rates and lowers gross private investment in an economy, it is called the:
a. countercyclical effect.
b. policy lag effect
c. multiplier effect.
d. crowding out effect.
d
You might also like to view...
The above figure depicts the Edgeworth box for two consumers, Al and Bruce. Explain why point "a" cannot be a competitive equilibrium
What will be an ideal response?
Since the Federal Reserve was established in 1913, the U.S. has experienced three periods of high inflation and each was preceded and accompanied by a period of sharp decline in the money supply
a. True b. False Indicate whether the statement is true or false
Table 10.1 shows the cash flows and discounted cash flows for three mutually exclusive projects available to a company. Assume an interest rate of 5%. Which project has the highest internal rate of return?
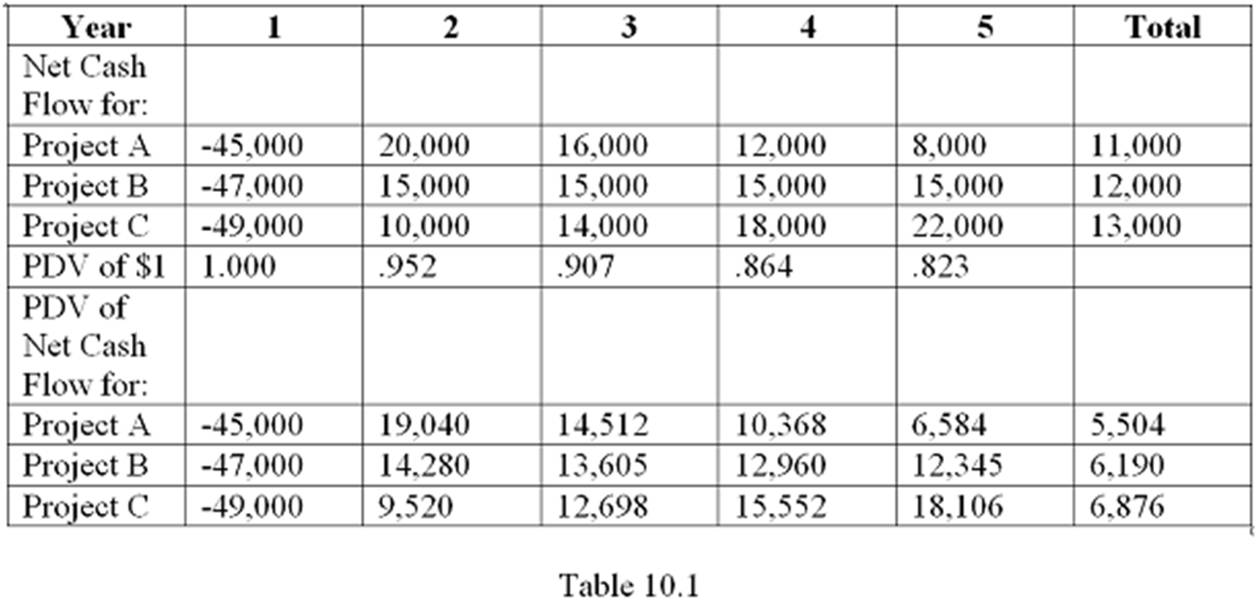
A. Project A
B. Project B
C. Project C
D. It cannot be determined from the information given.
If the federal funds rate were below the level the Federal Reserve had targeted, the Fed could move the rate back towards its target by
a. buying bonds. This buying would increase the money supply. b. buying bonds. This buying would reduce the money supply. c. selling bonds. This selling would increase the money supply. d. selling bonds. This selling would reduce the money supply.