What does it mean to say that an individual's preferences are transitive?
What will be an ideal response?
Consistency in the choices that an individual makes is referred to as transitivity. Preferences are transitive if the following is true: if an individual prefers choice A to choice B and choice B to choice C, then it is implied that she prefers choice A to choice C. Transitivity is considered a minimal requirement for rational decisionmaking because without it an individual could end up in an infinite and frustrating cycle. If the individual's choices were not transitive, she would first choose Choice A over Choice B, then Choice B over Choice C, but then opt for Choice C over Choice A, which is inconsistent with her earlier choices.
A-head: CONFLICT OF INTEREST AND POLITICAL ECONOMY
Concept: Transitive preferences
You might also like to view...
Paradoxically, when the economy most needs injections of money, the economic conditions are such that
a. borrowers are particularly eager to go to banks for loans b. borrowers are most reluctant to borrow (demand loans) from banks c. the FDIC will insist that banks raise the interest rate they charge borrowers d. the FSLIC and FDIC will insist that banks lower the interest rate they charge borrowers e. the Federal Reserve will print less money
Technology is an important factor in explaining the high incomes of some athletes primarily because
a. technology accounts for differences in incomes within all occupations. b. technology makes it possible for very large numbers of people to watch athletes perform. c. technology improves the performance of athletes. d. technology requires human capital to use it efficiently.
Suppose Chris is a potter who makes mugs. His total costs depend on the number of mugs he makes each day, as shown in the accompanying table.Number of Mugs Per DayTotal Cost Per Day0$101$142$193$254$325$406$49 If the market for mugs is perfectly competitive, and mugs sell for $7.50 each, then Chris should make ________ mugs per day.
A. 4 B. 5 C. 6 D. 0
In the Aggregate Demand - Aggregate Supply diagram in Figure 8.1, Box 2 should be filled with 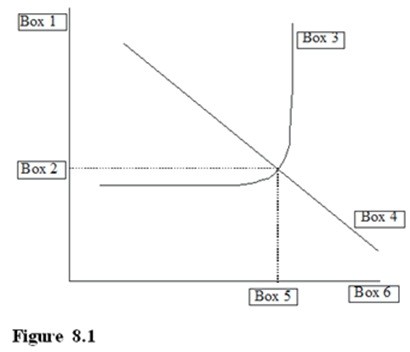
A. AD for Aggregate Demand. B. AS for Aggregate Supply. C. PI* for macroeconomic equilibrium Price Index. D. RGDP* for macroeconomic equilibrium Real Gross Domestic Product.