Describe the properties, current atmospheric concentrations, and sources the primary greenhouse gases contributing to climate change?
What will be an ideal response?
Answers should include the following gases:
Water vapor (H2O): most abundant, but low residence time. Natural sources.
Carbon dioxide (CO2): greatest contributor; long residence time; anthropogenic sources and natural sources. Currently 400 ppm.
Methane (CH4): high global warming capacity; intermediate residence time; high global warming potential; largest sources are anthropogenic; 750 ppb.
Nitrous oxides (N2O): higher than any time in the last 100,000 years. long residence time; high global warming potential; emissions associated with agriculture contribute to rise, but also some natural sources.
Halogens (CFCs, etc.): 100% anthropogenic; high global warming potential, but greatly reduced due to Montreal Protocol.
You might also like to view...
If the dry-bulb temperature is 32°C and the wet-bulb temperature is 26°C, What is the relative humidity?
Using the psychrometer tables and the table of saturation mixing ratios, answer the question about determining relative humidity with a sling psychrometer. __________ %
Which of the following molecules is not a straight-chain hydrocarbon?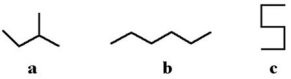
A. a B. b C. c D. All of the above are straight-chain hydrocarbons. E. None of the above are straight-chain hydrocarbons.
Slack water occurs ____
A) at high tide B) at low tide C) when the current is changing direction D) when water starts rushing out
mP air masses over the northeastern United States produce stable, clear skies in the summer and heavy snowstorms in the winter
Indicate whether the statement is true or false