The figure below shows an IS-LM-FE model for an economy with fixed exchange rates. Initially the economy is at Point A, a triple intersection. Here, the FE curve is steeper than the LM curve.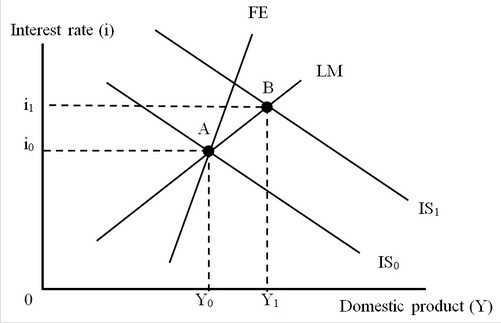 Assume that the economy was initially at Point A. Which of the following could have caused the economy to move to and remain at Point B?
Assume that the economy was initially at Point A. Which of the following could have caused the economy to move to and remain at Point B?
A. Expansionary monetary policy with sterilization
B. Contractionary fiscal policy without sterilization
C. Expansionary monetary policy without sterilization
D. Expansionary fiscal policy with sterilization
Answer: D
You might also like to view...
When obtaining information is costly, competition is
A) less effective at forcing prices down. B) more effective at forcing prices down. C) only effective at forcing prices u
An economic model suggests that an additional year of education increases a student's future wages by 15 percent. Using this model, answer the following questions: a) Gary completes 8 years of education, and John completes 9 years of education
If Gary earns $20 per hour, how much is John expected to earn? b) John completes 9 years of education, and Kevin completes 12 years of education. Given John's earnings [as calculated in a)], how much is Kevin expected to earn? c) Is there any limitation to such a model? Explain your answer.
In the United States, the smallest source of expenditure on healthcare is
A) government expenditure. B) private insurance expenditure. C) out-of-pocket expenditure. D) unknown.
A firm can minimize cost by
A) picking the bundle of inputs where the lowest isocost line touches the isoquant. B) picking the bundle of inputs where the isoquant is tangent to the isocost line. C) picking the bundle of inputs where the last dollar spent on one input gives as much extra output as the last dollar spent on any other input. D) All of the above.