A profit-maximizing monopolist
A. engages in more research and development activity than a perfectly competitive firm.
B. produces the output level where P = MC.
C. produces less output than a perfectly competitive industry.
D. produces at the unit elastic point on the market demand curve.
Answer: C
You might also like to view...
Growth in the Solow residual was slowest in the
A) 1950s. B) 1960s. C) 1970s. D) 1980s.
Which of the following must be included in an organization’s statement of accounting profits for the statement to be of use?
a. the estimated amount the organization could have earned pursuing other options b. the extent to which technological improvements increased productivity c. the percentages planned for reinvestment or distribution to investors d. the period in which the profit was earned, such as a year or a quarter
Figure 5-17
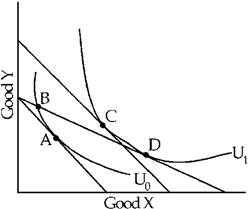
Which of the following statements about Figure 5-17 must be correct?
a.
The consumer pays a higher dollar price per unit for good Y at A than at D.
b.
The consumer pays the same dollar price per unit for good Y at A and at B.
c.
The consumer pays a higher dollar price per unit for good X at D than at A.
d.
The consumer pays a higher dollar price per unit for good X at A than at C.
Which of the following statements best describes the price, output, and profit conditions of monopolistic competition?
A. Price will equal marginal cost at the profit-maximizing level of output; profits will be positive in the long-run. B. Price will always equal average variable cost in the short run and either profits or losses may result in the long run. C. Marginal revenue will equal marginal cost at the short run, profit-maximizing level of output; in the long run, economic profit will be zero. D. Marginal revenue will equal average total cost in the short run; long-run economic profits will be zero.