When price is $6
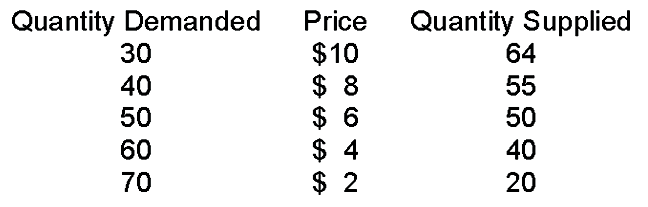
A. there is a surplus.
B. there is a shortage.
C. there is both a surplus and a shortage.
D. there is neither a surplus nor a shortage.
D. there is neither a surplus nor a shortage.
You might also like to view...
Keynesian economics predicts that if government policy makers deem current equilibrium real Gross Domestic Product (GDP) to be "too low," then an appropriate policy action would be to
A) do nothing, because the economy is self-adjusting. B) raise government spending, thereby increasing aggregate demand and pushing up real Gross Domestic Product (GDP) with little or no inflationary consequences. C) increase taxes, thereby causing aggregate demand to increase and inducing a rise in real Gross Domestic Product (GDP) with little or no inflationary consequences. D) reduce the money stock, thereby causing aggregate demand to decrease and inducing a rise in fall in the price level that generates an increase in total planned expenditures.
When banks create money, they
a. increase wealth at a pace equal to the rate of money creation b. destroy wealth at a pace equal to the rate of money creation c. increase wealth at a rate exceeding the rate of money creation d. increase wealth at a rate less than the rate of money creation e. do not create wealth
Investment A pays $1,200 half of the time and $800 half of the time. Investment B pays $1,400 half of the time and $600 half of the time. Which of the following statements is correct?
A. Investment A and B have the same expected value, but A has greater risk. B. Investment A has a greater expected value than B, but B has less risk. C. Investment B has a higher expected value than A, but also greater risk. D. Investment A and B have the same expected value, but A has lower risk than B.
Comparative advantage is
A) the ability to produce more output from given inputs than another producer can. B) the ability to produce a good at a lower opportunity cost than other producers. C) the ability to produce more output of all goods than anyone else can. D) the ability to produce all goods at lower costs than anyone else can.