Two identical conducting spheres A and B carry equal charge and exert electrostatic forces of magnitude F on each other. They are separated by a distance much larger than their diameters. A third identical conducting sphere C is uncharged. Sphere C is first touched to A, then to B, and finally removed. As a result, the electrostatic force between A and B becomes:
A) F/2
B) F/4
C) 3F/8
D) F/16
E) 0
C) 3F/8
You might also like to view...
Could our Sun ever undergo a nova or a white dwarf supernova event? Why or why not?
What will be an ideal response?
As a general rule, there is a(n) __________ relationship between increased stream order and stream size
What will be an ideal response?
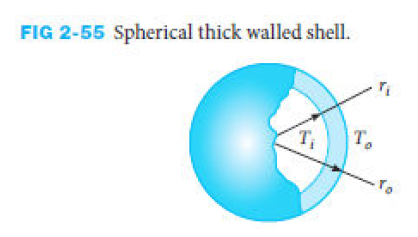
Write the governing equation and the necessary boundary conditions for the problem of a spherical concrete shell as sketched in Figure 2-55.
Dielectrics: An air-filled capacitor carries enough charge to store 6.00 mJ of potential energy. It is then accidentally filled with water in such a way as not to discharge its plates. How much energy does it continue to store after it is filled? The dielectric constant for water is 78 and for air it is 1.0006.
A. 0.077 mJ B. 468 mJ C. 0.04 mJ D. 6.00 mJ