How is the bulk of carbon dioxide transported in blood?
A) as carbonic acid in the plasma
B) as bicarbonate ions in plasma after first entering the red blood cells
C) chemically combined with the heme portion of hemoglobin
D) chemically combined with the amino acids of hemoglobin as carbaminohemoglobin in the red blood cells
B
You might also like to view...
The only role of modulator molecules is to enhance the binding affinity of the functional site of an allosteric protein.
Answer the following statement true (T) or false (F)
The ________ regulates smoothing of transitions from inspiration to expiration.
Fill in the blank(s) with the appropriate word(s).
Using Figure 24.2, match the following:
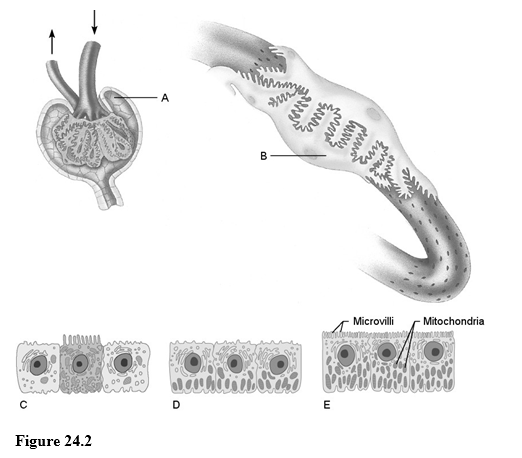
1) Podocyte.
2) Is composed of simple squamous epithelium.
3) Collecting duct cells.
4) Proximal convoluted tubule cells.
5) Filtrate at the site of these cells is about the same osmolarity as blood plasma.
6) Cells that are the most active in reabsorbing the filtrate.
7) Cells that reabsorb virtually all the nutrients.
8) Cells that are most affected by ADH.
9) Almost no water is absorbed in these cells.
The membranous lining of the abdominal cavity is called the:
A) mediastinum B) pleura C) peritoneum D) pericardium E) periabdominus