The more powerful the motor is
a. the longer the time interval for doing the work is.
b. the shorter the time interval for doing the work is.
c. the greater the ability to do the work is.
d. the shorter the workload is.
Ans: b. the shorter the time interval for doing the work is.
You might also like to view...
A hot-wire anemometer is used to determine the boundary layer velocity profile in the air flow over a scale model of an automobile. The hot-wire is held in a traversing mechanism that moves the wire in a direction normal to the surface of the model. The hot-wire is operated at constant temperature. The boundary layer thickness is to be defined as the distance from the model surface at which the velocity is 90% of the free stream velocity. If the probe current is I0, when the hot-wire is held in the free stream velocity, U?, what current indicates the edge of the boundary layer? Neglect radiation heat transfer from the hot-wire and conduction from the ends of the wire.
GIVEN • Thin, electrically-heated constant-temperature wire in air flow near an automobile model • Boundary layer thickness ° point when velocity (Uy) = 90% free stream velocity Vo • Probe current at U? = Io FIND • Probe current at edge of the boundary layer (Ib) ASSUMPTIONS • Radiation is negligible • Conduction from the ends of the hot-wire is negligible • Reynolds number is small
What are beats and how are they produced?
What will be an ideal response?
An ideal gas is at a temperature of 40 and a pressure of 2.00 atmospheres. If the diameter of an N2 molecule is 0.300 nm, then what is the mean free path of the N2 molecule in the gas?
and a pressure of 2.00 atmospheres. If the diameter of an N2 molecule is 0.300 nm, then what is the mean free path of the N2 molecule in the gas?
a. 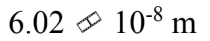
b. 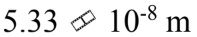
c. 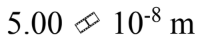
d. 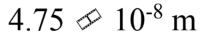
e. 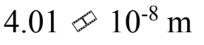
Given the equation 
A. A 3.00-kg mass is suspended from the ceiling. B. A 2.00-kg mass hanging over a pulley drags a 3.00-kg mass along a frictionless horizontal surface. C. A 3.00-kg mass hanging over a pulley drags a 2.00-kg mass along a frictionless horizontal surface. D. A 3.00-kg mass hanging over a pulley drags a 5.00-kg mass along a frictionless horizontal surface. E. A 5.00-kg mass hanging over a pulley drags a 3.00-kg mass along a frictionless horizontal surface.