In regulating a natural monopoly, the price strategy that ensures the highest possible output and zero profit is one that sets price
A) equal to average total cost where it intersects the demand curve.
B) equal to marginal cost where it intersects the demand curve.
C) equal to average variable cost where it intersects the demand curve.
D) corresponding to the demand curve where marginal revenue equals zero.
Answer: A
You might also like to view...
In the table above, the marginal benefit of the 4 millionth television set is
A) negative 0.5 computers per television set. B) 0.25 computers per television set. C) 0.5 computers per television set. D) 1.0 computer per television set.
If each player has a dominant strategy, then those strategies make up the Nash equilibrium
What will be an ideal response?
We expect the demand curve in the perfectly competitive industry to be
a. negatively sloped. b. vertical. c. horizontal. d. perfectly elastic.
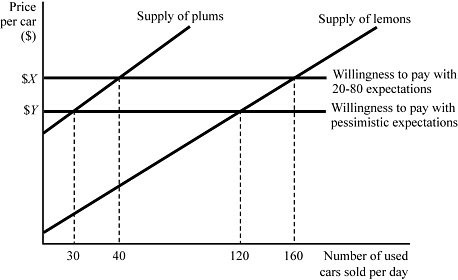
 Figure 9.5 represents the market for used cars. Suppose buyers are willing to pay $5,000 for a plum (high-quality) used car and $3,000 for a lemon (low-quality) used car. If buyers believe that 80% of used cars in the market are lemons (low quality), what percent of used cars sold will actually be plums?
Figure 9.5 represents the market for used cars. Suppose buyers are willing to pay $5,000 for a plum (high-quality) used car and $3,000 for a lemon (low-quality) used car. If buyers believe that 80% of used cars in the market are lemons (low quality), what percent of used cars sold will actually be plums?
A. 20% B. 25% C. 33.33% D. 75%