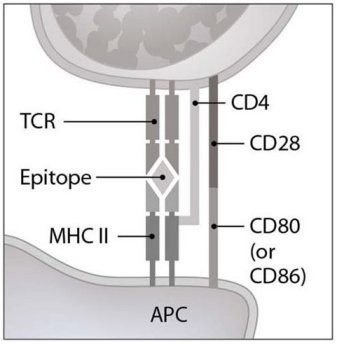
 Figure 16.2 illustrates an interaction between a(n)
Figure 16.2 illustrates an interaction between a(n)
A. antigen presenting cell and a B lymphocyte.
B. antigen presenting cell and a helper T lymphocyte.
C. NK cell and its target cell.
D. cytotoxic T lymphocyte and its target cell.
E. antigen presenting cell and a plasma cell.
Answer: B
You might also like to view...
Which of the following is NOT true about
overactive alcohol dehydrogenase (ADH)?
a. the effects are the same as the effects of underactive ALDH b. people with overactive ADH can handle only small amounts of alcohol c. it causes an excess accumulation of acetaldehyde d. it is common in people of Asian descent e. people with overactive ADH are more likely to become alcoholics
A chromosome has broken, and a piece of one chromosome is translocated to a non-homologous chromosome. This is an example of what type of chromosomal alteration?
A) paracentric inversion B) dicentric bridge C) unbalanced translocation D) Robertsonian translocation E) inversion loop
After a haploid spore germinates, if then complete mitosis, forming hyphae. The resulting hyphae are
A. diploid. B. dikaryotic. C. zygotes. D. gametes. E. haploid.
In the light-independent reactions, when CO2 is added to a molecule of Ribulose 1,5-bisphosphate (RuBP), the immediate product is
A. citric acid. B. 3-phosphoglycerate. C. glyceraldehyde-3-phosphate. D. glucose. E. pyruvate.