Intertemporal substitution dictates that
a. people will work less in periods of high productivity.
b. people will spend more in periods of high productivity.
c. people will work more in periods of high productivity.
d. people will spend less in periods of high productivity.
c. people will work more in periods of high productivity.
You might also like to view...
Refer to the figure below. In response to gradually falling inflation, this economy will eventually move from its short-run equilibrium to its long-run equilibrium. Graphically, this would be seen as 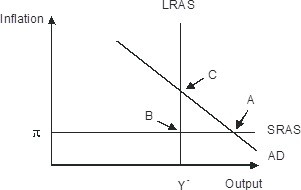
A. long-run aggregate supply shifting leftward B. Short-run aggregate supply shifting upward C. Short-run aggregate supply shifting downward D. Aggregate demand shifting leftward
Employers and workers in the protected industry know that the consequences of protection are principally:
a. lower prices for their output, lower profits for owners, and lower wages for workers. b. higher prices for their output, lower profits for owners, and lower wages for workers. c. higher prices for their output, lower profits for owners, and higher wages for workers. d. lower prices for their output, higher profits for owners, and higher wages for workers. e. higher prices for their output, higher profits for owners, and higher wages for workers.
If Q represents real GDP and P is the price level, then P × Q equals ______.
a. real NI b. real NNP c. nominal NNP d. nominal GDP
Since 1975, U.S. exports and imports have:
A. grown absolutely but remained a constant proportion of GDP. B. grown absolutely but declined as a proportion of GDP. C. grown both absolutely and as a percentage of GDP. D. declined both absolutely and as a percentage of GDP.