On January 1, a company issues bonds dated January 1 with a par value of $200,000. The bonds mature in 3 years. The contract rate is 4%, and interest is paid semiannually on June 30 and December 31. The market rate is 5%. Using the present value factors below, the issue (selling) price of the bonds is: n= i= Present Value of an Annuity(series of payments) Present value of 1(single sum)3 4.0% 2.7751 0.88906 2.0% 5.6014 0.88803 5.0% 2.7232 0.86386 2.5% 5.5081 0.8623
A. $205,607.
B. $172,460.
C. $194,492.
D. $22,032.
E. $200,000.
Answer: C
You might also like to view...
U.S. GAAP and IFRS require firms to disclose the fair value of financial instruments in a note to the financial statements. What should such a note include?
Refer to the data given in the table for Acme Widgets, Inc. Solve the transportation problem using Excel Solver. (Remember that in balanced transportation problems all constraints—except the non-negativity constraints of the decision variables—should be set as an equal to (=) sign in the Excel Solver dialogue.) At the optimum solution, the lowest non-zero quantity shipped is from ______.
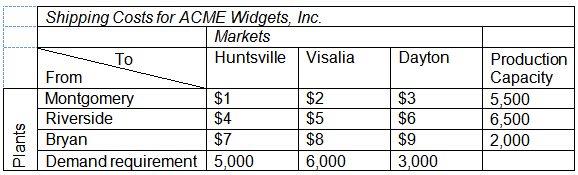
a. Montgomery to Visalia
b. Riverside to Visalia
c. Montgomery to Dayton
d. Bryan to Huntsville
The frequency with which losses occur and their severity are two key statistical measures for evaluating loss exposure
Indicate whether the statement is true or false
A student believes that the average grade on the statistics final examination was 87 . A sample of 36 past final examinations was taken. The average grade in the sample was 83.96 with a standard deviation of 12
a. State the null and alternative hypotheses. b. Using the critical value approach, test the hypotheses at the 5% level of significance. c. Using the p-value approach, test the hypotheses at the 5% level of significance.