How do atmospheric windows limit observations made from Earth's surface?
What will be an ideal response?
Because the atmosphere is opaque to certain parts of the electromagnetic spectrum, Earth-based telescopes are limited to the parts of the EM spectrum that can pass through the atmosphere.
You might also like to view...
Reconsider the heat exchanger and explore the effect of tube center-to- center spacing in the equilateral array of the finned tubes. Consider the tube spacing of 8.75 cm and 10 cm. What is the extent of change in the average heat transfer coefficient and pressure drop? Likewise, what is the extent of change in the thermal and hydrodynamic performance if a square pitch (inline arrangement is considered) with tube center-to-center spacing of 7.5 cm?
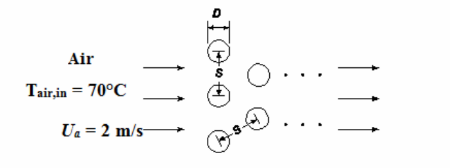
GIVEN
Heated air flowing over an equilateral staggered tube bank
Exhaust gas temperature
Tair,in = 400°C
Number of tube rows (NL) = 10
Tube diameter (D) = 2.5 cm= 0.025 m
Center to center pitch(S) = 7.5 cm=0.075 m
Free stream velocity (Ua) = 2 m/s
Tube surface temperature (Tt) = 175°C
Finned surface extension ration (?)= 1.15
FIND
The average heat transfer coefficient (c h) and pressure drop in gas flow stream.
ASSUMPTIONS
Steady state
Tube wall temperature is uniform and constant
SKETCH
An ideal gas is allowed to expand slowly at constant temperature to twice its original volume. During the expansion, the gas absorbs 200 kJ of heat
(a) What is the change in the internal (thermal) energy of the gas during the expansion? (b) How much work does the gas do during the expansion?
A car heading north collides at an intersection with a truck of the same mass as the car heading east. If they lock together and travel at 28 m/s at 46° north of east just after the collision,
how fast was the car initially traveling? Assume that any other unbalanced forces are negligible. A) 40 m/s B) 80 m/s C) 30 m/s D) 20 m/s
Two spheres, one hollow and one solid, are rotating with the same angular speed around an axis through their centers. Both spheres have the same mass and radius. Which sphere, if either, has the higher rotational kinetic energy?
1.the hollow sphere 2.the solid sphere 3.They have the same kinetic energy.1