Economists cite some beneficial effects of price discrimination. What are these benefits and how do the antitrust laws treat price discrimination?
Benefits include the ability to sell a product at a low price to low-income consumers, while charging a higher price to high-income consumers. Even the wealthy may pay less than if discrimination were disallowed, since profits in the low-income market might permit a lower price in the high-income market. The Robinson-Patman Act (1936) and the Clayton Act (1914) generally discourage price discrimination.
You might also like to view...
Chain-weighted price indices are constructed such that
A) all years' levels of GDP are directly related to a base year level of GDP. B) prices of one good can be directly compared with prices of other goods. C) prices in different years can be directly compared with one another. D) prices in different economies can be directly compared with one another.
Refer to the table above. The private sector balance is a
A) $700 billion surplus. B) $400 billion deficit. C) $700 billion deficit. D) $2,900 billion deficit. E) $2,900 billion surplus.
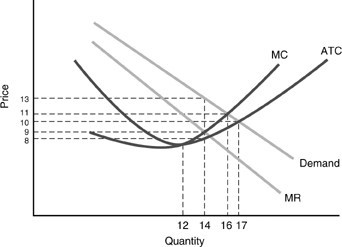 In the above figure, what is total revenue at the profit-maximizing point?
In the above figure, what is total revenue at the profit-maximizing point?
A. $170 B. $176 C. $126 D. $182
Refer to the diagram in which S is the before-tax supply curve and S t is the supply curve after an excise tax is imposed. The efficiency loss of the tax is shown by areas:
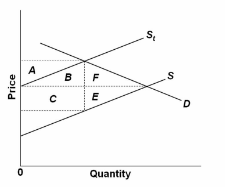
A. A + B + C + E + F.
B. A + B + C.
C. A + B + F.
D. E + F.