Suppose that government regulators required a natural monopoly to charge a price equal to the marginal cost of the last unit produced. Which of the following would then be true?
a. The natural monopoly would earn zero economic profits but consumers would benefit from the low regulated price. The low price would sustain long-run production of the firm.
b. The natural monopoly would be allocatively efficient but would suffer economic losses. It would be unable to sustain itself in the long run.
c. The natural monopoly would be allocatively efficient and would earn positive economic profits. Consumer surplus would increase significantly.
d. The natural monopoly would be allocatively inefficient but earn positive economic profits. Consumer surplus would reduce significantly.
b
You might also like to view...
If real GDP is $10 trillion and the velocity of circulation is 2, the quantity of money
A) is $2 trillion. B) is $5 trillion. C) is $20 trillion. D) cannot be determined from the information given.
In a study of college yearbook photos, researchers found that:
a. An inauthentic smile by males meant they would be unhappy in life b. Women with the Pan Am (fake) smile were just as happy in life as women with the Duchene (genuine) smile c. Smiling type makes no difference d. A genuinely smiling woman (with the Duchene smile) is more likely to be married, stay married, and to experience more personal well-being than a woman with the fake smile.
Assume the market is in equilibrium in the graph shown at demand D and supply S1. If the supply curve shifts to S2, and a new equilibrium is reached, equilibrium quantity will increase from 4 to 4.5 units. Which of the following is true?
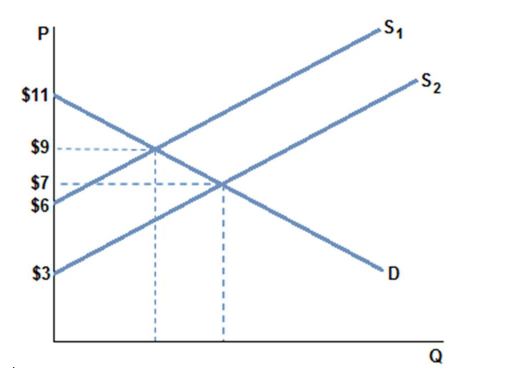
A. Producer surplus increases by $3.00.
B. Producer surplus decreases by $8.50.
C. Producer surplus increases by $7.50.
D. Producer surplus decreases by $16.
The essential functions of any central bank are:
A. preventing the formulation of monopolies or other market failure, and acting as a lender of last resort. B. managing the money supply, and acting as a lender of last resort. C. overseeing major business transactions, and managing the money supply. D. collecting taxes, and managing the supply of money.