When an object moves close to the speed of light relative to Earth, what happens to its dimensions compared to what they were before it began moving, as measured by an Earth-based observer?
A) Only lengths parallel to the direction of travel are decreased.
B) Only lengths perpendicular to the direction of travel are decreased.
C) All lengths are decreased.
D) No lengths are affected.
A
You might also like to view...
The figures below represent interference fringes. The distances from the screen to the slits is the same for each figure, and the planes of the screen and the slits are parallel. In each figure the spacing d between the slits is the same. Which figure(s) represent(s) slits illuminated with light of the shortest wavelength ?? The white spaces represent the interference maxima.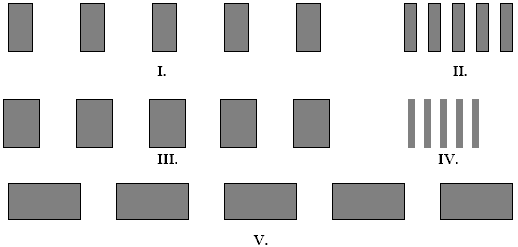
A. I. B. II. C. III. D. IV. E. V.
What inductance must be put in series with a 100-k? resistor at 1.0-MHz for a total impedance of 150 k??
A) 18 mH B) 1.5 H C) 0.17 H D) 0.15 H
Which of the following would NOT cause the gravitational force on an object near Earth's surface to increase?
A. an ore deposit just under the surface B. a lower elevation C. an increase in its mass D. a horizontal velocity
Which of these is an accurate statement of Newton's first law?
a. An object at rest tends to remain at rest. b. An object in motion tends to remain in motion. c. An object with no force acting along its direction of motion tends to move in a circle at constant speed. d. In the absence of an unbalanced force, the velocity of an object remains constant. e. In the absence of an unbalanced force, the speed of an object remains constant.