When it comes to public goods, it is important to remember
A. the free rider problem is difficult to overcome, but the drop-in-the-bucket problem is not.
B. all goods provided by the government are public goods.
C. that government intervention necessarily solves the market failure.
D. only one level of output can be realized, and consumers are willing to pay different amounts for that level.
Answer: D
You might also like to view...
The following table provides nominal exchange rates for the U.S. dollar.CountryForeign currency/dollarDollar/foreign currencyCanada(Canadian dollar)1.488.672Mexico(Peso)9.259.108Based on these data, the nominal exchange rate equals approximately ________ pesos per Canadian dollar or, equivalently, ________ Canadian dollars per peso.
A. 9.259; 0.108 B. 7.771; 0.129 C. 0.672; 1.488 D. 6.222; 0.161
The supply curve illustrates
A) the amount of a good producers plan to sell at given prices. B) the amount of a good producers need to sell at given prices. C) the corresponding demand for a good at given prices. D) the sunk costs associated with producing a scarce good.
When a reduction in the price of a good allows a consumer to purchase more of all goods, this effect is called the:
a. income effect. b. substitution effect. c. elasticity effect. d. monetary effect.
Refer to the information provided in Table 8.1 below to answer the question(s) that follow.
Table 8.1 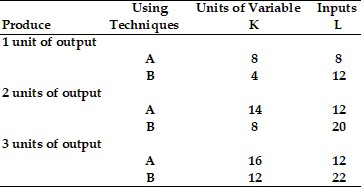 Refer to Table 8.1. Assuming the price of labor (L) is $5 per unit and the price of capital (K) is $10 per unit, what production technique should this firm use to produce 2 units of output?
Refer to Table 8.1. Assuming the price of labor (L) is $5 per unit and the price of capital (K) is $10 per unit, what production technique should this firm use to produce 2 units of output?
A. production technique A B. production technique B C. The firm is indifferent between production technique A and production technique B. D. It is impossible to determine if the firm should select production technique A or B because total fixed costs are not given.