How did dark matter behave differently from normal matter during the early stages of the big bang, and how is this important for the formation of stars and galaxies?
What will be an ideal response?
As long as radiation dominated the early Universe, normal baryonic matter could not contract to form galaxies and stars. Dark, non-baryonic matter does not interact with electromagnetic radiation, and was not affected by the intense radiation.
Tiny fluctuations in the texture of the big bang were caused by quantum mechanical effects. As the Universe expanded, these tiny fluctuations would have been stretched to very large, but subtle, variations in the gravitational field of the Universe. Since dark matter was not affected by radiation, it began to clump around areas of higher gravitational field.
At the time of recombination, baryonic matter was smoothly spread through the Universe, but dark matter was already clumped in filaments. After recombination, ordinary matter quickly gravitated to regions of high dark-matter density.
Dark matter clumping allowed normal matter to clump and begin producing stars and galaxies much faster than normal matter could have done on its own.
You might also like to view...
Latent Heats: The figure shows a graph of the temperature of a pure substance as a function of time as heat is added to it at a constant rate in a closed container. If LF is the latent heat of fusion of this substance and LV is its latent heat of vaporization, what is the value of the ratio LV/LF?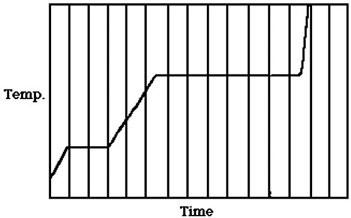
A. 5.0 B. 4.5 C. 7.2 D. 3.5 E. 1.5
Suppose that you measure the parallax angle for a particular star to be 0.1 arcseconds. What is the distance to this star? (Hint: A star at a distance of 3.26 light-years has a parallax angle of 1.0 arcseconds.)
A) 0.1 light-years B) 0.326 light-years C) 10 light-years D) 32.6 light-years E) 3.26 light-years
An electron moving in the positive x direction experiences a magnetic force in the positive z direction. If Bx = 0, what is the direction of the magnetic field?
A. negative y direction B. positive y direction C. negative z direction D. positive z direction E. negative x direction
What is the advantage of the steam trap?