All industrialized countries have become “service economies” in recent decades. Explain the reasons behind this shift.
What will be an ideal response?
To a considerable degree, this shift to services reflects the arrival of the “Information Age.” Activities related to computers, to research, to the transmission of information by teaching and publication, and other information-related activities are providing many of the new jobs. Technological change has also made it possible to produce more and more manufactured products using fewer and fewer workers. Such laborsaving innovation in manufacturing has allowed a considerable share of the labor force to move out of goods-producing jobs and into services.
You might also like to view...
Why do economists care about aggregate expenditures?
What will be an ideal response?
It costs a firm $80 per unit to produce product A and $50 per unit to produce B individually. If the firm can produce both products together at $120 per unit of product A and B, this exhibits signs of
a. Economies of scale b. Economies of Scope c. Diseconomies of Scale d. Diseconomies of Scope
When a bank receives new deposits, it can make new loans up to the amount of
A) the deposits received. B) the excess reserves generated by the deposits C) the reserves generated by the deposits. D) the required reserves generated by the deposits.
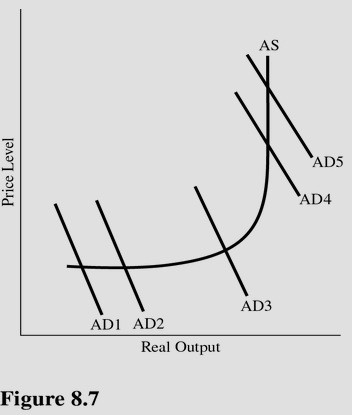 Using Figure 8.7, a shift in aggregate demand from AD4 to AD5 is most likely to cause
Using Figure 8.7, a shift in aggregate demand from AD4 to AD5 is most likely to cause
A. An increase in real output but no change in the price level. B. An increase in price level but no change in real output. C. A decrease in price level but no change in real output. D. An increase in real output and an increase in the price level.