When consumers would have been willing to pay higher prices at various quantities consumed than the market clearing price, the differences are called
A) consumer surplus.
B) monopoly profits.
C) opportunity cost.
D) deadweight loss.
A
You might also like to view...
If pollutants emitted by firms in the steel industry increase, but there is no increase in the costs borne by these firms, you could conclude that
a. pollution is not a serious problem in this industry. b. the consumers of steel are unwilling to bear the costs of pollution generated from steel production. c. pollution is an externality in this market, since producers and purchasers of steel do not bear the full costs of the pollution. d. pollution creates an external benefit rather than an external cost in this case.
Which of the following statements is correct?
a. Compensating wage differentials reflect different skills of workers. b. Discrimination by employers affects the marginal productivity of workers. c. The signaling theory of education suggests that schooling does not affect worker productivity. d. The superstar phenomenon explains why more talented entertainers earn more than less talented entertainers.
A politician, who wants to receive the maximum number of votes, spends 9 hours a week speaking to various groups. The table below shows his estimates of how time spent with each group will affect the number of votes he receives: 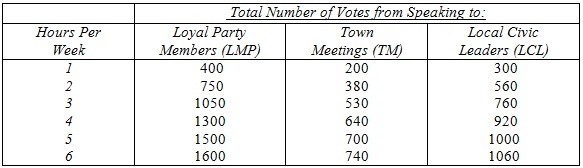 Based on the information above, how should the politician allocate his speaking time?
Based on the information above, how should the politician allocate his speaking time?
A. 5 hours to LPM, 2 hours to TM, 2 hours to LCL B. 4 hours to LPM, 2 hours to TM, 3 hours to LCL C. 5 hours to LPM, 1 hours to TM, 3 hours to LCL D. 3 hours to LPM, 3 hours to TM, 3 hours to LCL
Suppose the constant marginal cost of producing an automobile is $11,000 in Canada, $8,000 in the United States, and $12,000 in Japan. Each country's automobile industry is perfectly competitive.a. Under free trade, would Canada produce its own cars or import them? If it imports, which country will it import from?b. If the Canadian government imposes a 100 percent tariff on all auto imports, would it produce its own automobiles or import them? If it imports, which country will it import from?c. Canada has a tariff of 100 percent on imported autos. Then Canada decides to join a customs union with the United States (with a uniform external tariff of 100 percent). After the customs union is formed, what will the domestic price of automobiles be in Canada?d. If Canada decides to join this
customs union with the United States, will there be trade creation, trade diversion, or both? Explain. What will be an ideal response?