Use a leaky bucket to discuss the trade off between income equality and economic efficiency
What will be an ideal response?
If society decides to transport water (income) from the higher-income groups to lower-income groups, then it can do so in a bucket. The bucket, however, has some leaks that represent the loss in productive output that comes from reduced incentives to work, save, or invest by both groups, and from losses arising from the bureaucratic cost of managing the programs. Society must decide how much leakage from the bucket it will accept in the effort to redistribute income.
You might also like to view...
How do income and wealth change over a person's lifetime? How does this affect the distribution of income at a point in time?
What will be an ideal response?
Suppose the inverse demand curve for good A is given by the equation P A = 10 - Q A /10, and the supply curve is perfectly elastic (horizontal) at $1. Good A is presently taxed at $2 per unit. Good B (which is independent of good A) has an inverse demand curve, P B = 5 - Q B /20, and is also perfectly elastic at $1. Good B is untaxed.
(A) How much tax revenue is collected and what is the excess burden of the $2 tax on A? (B) How much revenue is collected if the tax on good A is reduced to $1 per unit and good B is taxed at $1 per unit? (C) What is the total excess burden of taxing both goods at $1 per unit? (D) Which tax system is preferable from the point of view of economic efficiency?
An artificially scarce good is:
A. not rival in consumption, but excludable. B. rival in consumption, but not excludable. C. rival in consumption and excludable. D. not rival in consumption and not excludable.
Refer to the figure below. What might cause shift from the original supply curve to the new supply curve? 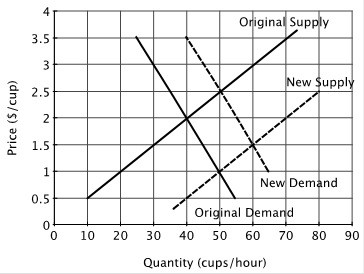
A. A news report that coffee consumption increases longevity. B. A new technology that reduces amount of coffee beans needed to make a good cup of coffee. C. A storm in that wipes out a large part of the coffee crop. D. An increase in the price of tea.