Consider a stock with a 50 percent probability of zero net earnings and a 50 percent probability of net earnings equal to $20 per share each year continuously in the future. Furthermore, assume that people are risk averse. That is, they will have to be compensated for uncertainty accompanying variation in their future wealth. If the interest rate were 5 percent, how much would people be willing
to pay for a share of this stock?
a. $10
b. $200
c. less than $200
d. more than $200
e. $400
C
You might also like to view...
Refer to Horizontal Merger. If area F + G is larger than area E, we can conclude that the horizontal merger
The following questions refer to the accompanying diagram, which shows the effects of a horizontal merger. Before the merger, the firm behaves competitively producing Q0 and charging P0. The merger lowers the firm's marginal cost and gives the firm enough market power to switch to the monopoly equilibrium.
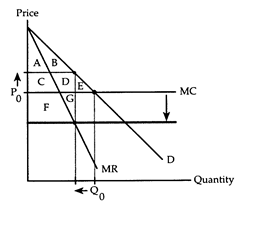
a. will reduce economic efficiency.
b. causes both consumers' and producer's surplus to rise.
c. will not increase the firm's profit and thus will not be undertaken.
d. creates an increase in social gain.
A general formula for the multiplier is
A) 1/(1-MPS) B) 1/(MPC) C) 1/(MPS) D) 1/(MPC-1)
The federal government began issuing inflation-indexed Treasury bonds in
A) 1913. B) 1989. C) 1997. D) 2001.
What is likely to be the best approach to a recession that is expected to turn into an expansion in a short time?
(A) Do nothing and let the economy fix itself. (B) Use monetary policy to lower interest rates. (C) Use fiscal policy to lower interest rates. (D) Use monetary policy to raise interest rates.