In the long run, profits for a monopolistic competitor will be:
A. the same as the profits for a monopolist.
B. the same as the profits for a purely competitive firm.
C. slightly less than the profits of a monopolist.
D. slightly more than the profits of a purely competitive firm.
Answer: B
You might also like to view...
An optimal decision is one that chooses the most desirable from among all possibilities that are available.
Answer the following statement true (T) or false (F)
Which of the following periods was not characterized by inflation in the U.S. economic history?
a. 1917–1920 b. 1929–1933 c. 1947 d. 1978–1980 e. 1980–1989
Consider a consumer choosing between spending her money on food, F, or clothing, C. Assume that a unit of food and a unit of clothing have the same price, and that the consumer can afford a total of 20 units of either food or clothing. The benefit of food is given by B(F) = 100?F, with MB(F) = 50/?F. The benefit of clothing is given by B(C) = 25C, with MB(C) = 25. How many units of clothing should the consumer buy?
A. 0 B. 2 C. 4 D. 6
Refer to the graph shown.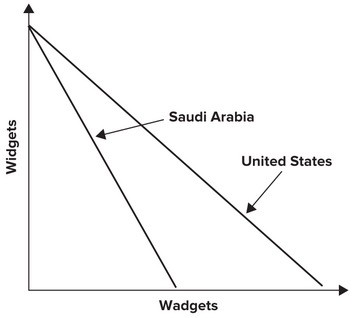 The graph demonstrates Saudi Arabia's and the United States' production possibility curves for widgets and wadgets. Given these production possibility curves, you would suggest that:
The graph demonstrates Saudi Arabia's and the United States' production possibility curves for widgets and wadgets. Given these production possibility curves, you would suggest that:
A. No trade should take place. B. Both countries should produce an equal amount of each. C. Saudi Arabia specialize in widgets and the United States in wadgets. D. Saudi Arabia specialize in wadgets and the United States in widgets.