A shift in union labor demand from D 1 to D 2 in the diagram might be the result of:
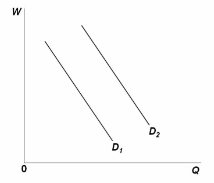
A. a refusal by union members to buy the product they are producing.
B. an increase in tariffs on products competing with those produced by relevant union workers.
C. increases in the prices of complementary inputs.
D. a strike (work stoppage) by the union.
B. an increase in tariffs on products competing with those produced by relevant union workers.
You might also like to view...
If a production process involved the creation of a negative externality, then the social cost of production would be:
A. larger than the private cost of production. B. the same as the private cost of production. C. smaller than the private cost of production. D. zero.
A seller's opportunity cost measures the
a. value of everything she must give up to produce a good. b. amount she is paid for a good minus her cost of providing it. c. consumer surplus. d. out of pocket expenses to produce a good but not the value of her time.
If the product produced by workers experiences a decrease in demand, the value of marginal product of labor will:
A. decrease, increasing the demand for labor. B. increase, increasing the demand for labor. C. decrease, decreasing the demand for labor. D. increase, decreasing the demand for labor.
If you own a bond with a seven percent coupon rate and new bonds are paying five percent, what will happen to your bond's market price?
What will be an ideal response?