Refer to the data. If year 2 is chosen as the base year, the price index for year 1 is:
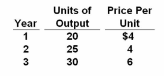
Assume an economy that is producing only one product. Output and price data for a three- year period are as follows. Answer the question on the basis of these data.
A. 80.
B. 100.
C. 120.
D. 20.
B. 100.
You might also like to view...
Adjustments in ________ take the economy from the short-run equilibrium to the long-run equilibrium
A) imports and exports B) wages and prices C) the multiplier D) interest rates
Labor unions
a. are formed to increase members' wages and improve working conditions. b. have represented a declining share of the workforce in the past 50 years. c. have traditionally found it difficult to organize workers in white-collar jobs. d. are characterized by all of the above.
A shoe manufacturer wants to maximize its total revenue. When the manufacturer charges $25 per shoe, consumers demand 50 shoes per day. The manufacturer knows that the demand for shoes is highly elastic. In the given scenario, which of the following statements is true?
a. To maximize total revenue, the manufacturer should decrease the price of its shoes, because the percentage increase in quantity demanded will more than offset the decrease in price. b. To maximize total revenue, the manufacturer should decrease the price of its shoes, because the percentage increase in quantity demanded will not offset the decrease in price. c. To maximize total revenue, the manufacturer should increase the price of its shoes, because the increase in price will more than offset the decrease in quantity demanded. d. To maximize total revenue, the manufacturer should increase the price of its shoes, because the increase in price will not offset the decrease in quantity demanded.
Suppose that a firm's long-run average total costs of producing small commuter jet airplanes increases as it produces between 2,000 and 4,000 airplanes. For this range of output, the firm is experiencing
a. economies of scale. b. constant returns to scale. c. diseconomies of scale. d. specialization.