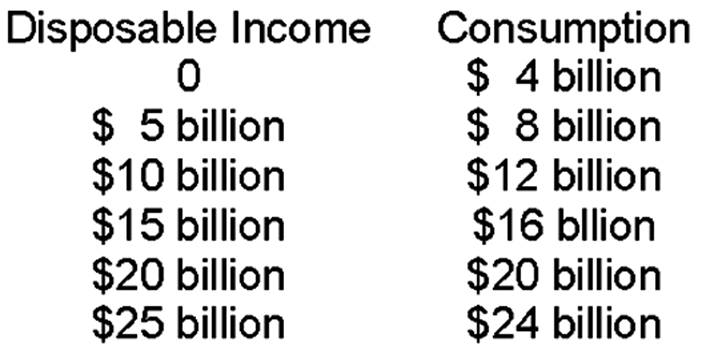Whenever a choice is made:
A) the value of all the other choices that could have been made is called opportunity cost.
B) normative economics is encountered.
C) the problem of "all other things unchanged" results.
D) the opportunity cost of that choice is the highest-valued other choice that could have been made.
Ans: D) the opportunity cost of that choice is the highest-valued other choice that could have been made.
You might also like to view...
Graph of the relationship between the prices in the supply schedule and the quantity supplied at those prices
What will be an ideal response?
Which of the following is not an example of Pareto optimality?
A. The city council approves a tax increase on all residents in order to make repairs to one remote residential street. B. The Beauregard twins eagerly switch cell phone cases with each other. C. Despite complaints from members, Harmony Industries builds a sewage treatment plant next to a country club. D. Timmy tricks Jonathan into trading a genuine Brooks Robinson baseball card for a fake Pete Rose baseball card.
The expected rate of return from an investment is:
A. Only the rate that compensates for time preference B. Only the rate that compensates for risk C. The rate that compensates for time preference plus the rate that compensates for risk D. The rate that compensates for time preference minus the rate that compensates for risk
How much is the MPS?