Follow a glucose molecule through aerobic respiration until all the energy that can be extracted is extracted
What will be an ideal response?
Respiration starts with glycolysis. During this process, the 6?carbon glucose is phosphorylated and oxidized into two 3?carbon sugar phosphates and eventually to two 3?carbon acids (pyruvates). Two ATPs are used in this process and four are produced for a net yield of two ATPs per glucose. The oxidations are coupled with the reductions of NAD+ to NADH. Each pyruvate is further oxidized to CO2 and acetyl?CoA, which can enter the Krebs cycle. This oxidation is also coupled with the reduction of NAD+ to NADH. In the Krebs cycle, acetyl?CoA donates its 2?carbon fragment to the 4?carbon acid, oxaloacetate to form the 6?carbon acid, citrate. Citrate is oxidized to a 5?carbon acid with the release of CO2 and the 5?carbon acid is oxidized to a 4?carbon acid with the release of another CO2 . The oxidations are coupled with the reductions of cofactors (NAD+ or FAD). One ATP is produced for each acetyl?CoA that enters the cycle. The 4?carbon acid is converted to oxaloacetate, and the cycle can start again. At this point, all the carbons in the original glucose have been converted to CO2 . The reduced cofactors from glycolysis and the Krebs cycle are sent to electron transfer chains where they are oxidized. The energy released by these oxidations is used to produce more ATP.
You might also like to view...
Discuss how the Human Microbiome Project will impact our understanding of human disease
What will be an ideal response?
How many amino acids are considered to be
essential because the human body cannot synthesize them? a. 2 b. 5 c. 8 d. 10 e. 12
Which portion of the accompanying figure would be connected to the oval window of the cochlea?
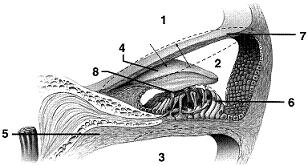
a. 1
b. 2
c. 3
d. 6
e. 8
In the pedigree shown, the individual indicated represents a(n)
a. healthy male. b. healthy female. c. affected male. d. affected female.