The conversion of solar energy into electric power by means of photovoltaic panels will be an important part of the transition from fossil fuels to sustainable energy resources. As described in detail in Principles of Sustainable Energy, a typical PV panel consists of a top layer of glass attached with a thin optically clear adhesive to a very thin layer of photoelectric material such as doped-silicon in which the incident solar irradiation is converted into electric energy. Experiments have shown that the solar to electric efficiency ?=0.55-0.001Tsilicon, where Tsilicon is the silicon temperature in K. In a typical installation where solar irradiation is G=700 W/m2, 7% is reflected from the top surface of the glass, 10% is absorbed by the glass, and 83% is transmitted to the
photovoltaic active layer. A part of irradiation absorbed by photovoltaic material is converted into heat and the remainder is converted into electric energy. The silicon layer is attached by a 0.01-mm thick layer of solder to a 3-mm thick aluminum nitride substrate as shown in the schemetic. Determine the electric power produced by this PV panel, assuming the following properties for the pertinent materials: conductivity of the glass kg=1.4 W/(m K), conductivity of the adhesive ka=145 W/(m K), the emmisivity of the glass is 0.90, heat transfer coefficient from the top of the panel to the surrounding is 35 W/(m2 K), and the surrounding air temperature is Tair=200C. The solar PV panel is 5 m long and 1 m wide and is situated on the roof where the bottom is considered insulated. (Hint: Start by applying first law of thermodynamics to the photovoltaic-active layer and note that some of the irradiation will be converted to electricity and some of it transmitted thermally)
GIVEN
• Electric efficiency ?=0.55-0.001Tsilicon
• Solar irradiation is G=700 W/m2
• Thickness of solder(ts=0.01 mm
• Al substrate thickness (tAl)=3 mm=0.003 m
• Conductivity of the glass kg=1.4 W/(m K)
• Conductivity of the adhesive ka=145 W/(m K)
• Emissivity of the glass is 0.90
• Heat transfer coefficient from the top of the panel to the surrounding(hc)= 35 W/(m2 K),
• Surrounding air temperature is Tair=200C.
• Solar PV panel area= 5 m*1m
FIND
Electric power produced by the PV panel.
ASSUMPTIONS
• 1 Dimensional steady state heat transfer
• Thermal conductivity remains constant.
SKETCH
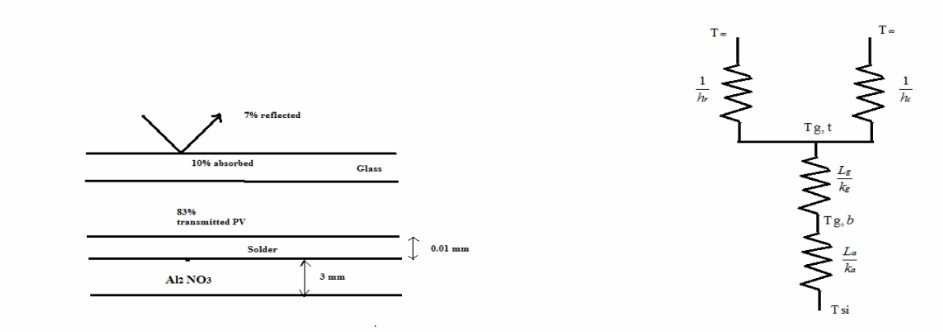
The energy which is not converted to electrical energy is transferred to the ambience through the adhesive and glass layer.
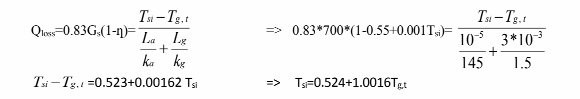
Also under steady state the heat transferred to the glass should be equal to total heat loss through glass to
ambience.

You might also like to view...
If a space heater consisted of a 10.0 cm radius iron ball through which electrical current was passed in order to heat the ball, what temperature would it need to be raised to in order to radiate 500 W into the surrounding air (which is at a temperature of 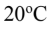 Assume the ball is a perfect blackbody.
Assume the ball is a perfect blackbody.
A. 510 K B. 346 K C. 730 K D. 530 K
What is the difference between hot spot volcanism and subduction zone volcanism?
What will be an ideal response?
Calculate the centripetal force on a 3.0-kg object moving in a horizontal circular path of 20-m radius with a speed of 8.0 m/s
Chromium-55 (54.9408 u) emits an electron leaving a daughter nucleus of manganese-55 (54.9380 u). How much energy is released in this reaction? (1 u = 931.5 MeV/c2)
a. 2.61 MeV c. 5.59 MeV b. 0.70 MeV d. 1.40 MeV