A reduction in the rate of population growth
A) always causes an increase in economic growth.
B) never causes an increase in economic growth.
C) may or may not cause an increase in economic growth.
D) will cause a reduction in economic growth if accompanied by an increase in the rate of growth of real GDP.
C
You might also like to view...
A grocery shopper considers "eliminating" the middleman. What might she do?
A) Raise her own cows, slaughter them, and butcher her own meat. B) Grow her own wheat, mill it into flour, and bake her own bread. C) Build her own fishing boat and begin halibut fishing. D) All of the above.
In long-run equilibrium, the perfectly competitive firm produces
a. where P = MC = AC. b. at the lowest point on its long-run average cost curve. c. where its long-run average cost curve is tangent to its horizontal demand curve. d. All of the above are correct.
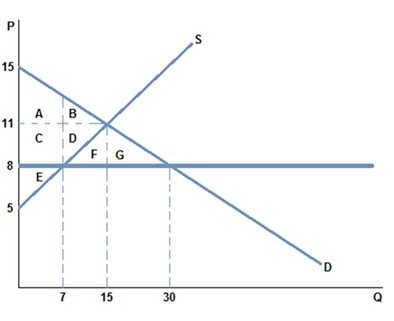 A binding price ceiling that could be set in the market in the graph shown would be:
A binding price ceiling that could be set in the market in the graph shown would be:
A. $15. B. $8. C. $11. D. $30.
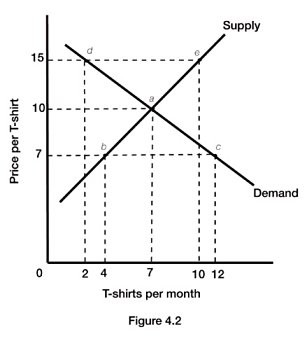 Figure 4.2 illustrates the supply and demand for t-shirts. If the actual price of t-shirts is $15, we would expect that:
Figure 4.2 illustrates the supply and demand for t-shirts. If the actual price of t-shirts is $15, we would expect that:
A. demand will decrease until quantity demanded equals quantity supplied. B. supply will increase until quantity demanded equals quantity supplied. C. price will decrease until quantity demanded equals quantity supplied. D. there will be no change in the price since the market is in equilibrium.